The Neurological Assessment in the NMC OSCE (Objective Structured Clinical Examination) is a crucial component in the subdural haematoma scenario during the Assessment station. To assess the neurological status of a patient systematically and safely, identifying any abnormalities or deterioration.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Purpose of the Neurological Assessment
A neurological assessment in the NMC OSCE helps in identifying any changes in the nervous system. It is a severe condition where blood collects between the skull and the brain’s surface. A head injury usually causes it. Symptoms of a subdural hematoma can include a headache that keeps getting worse.
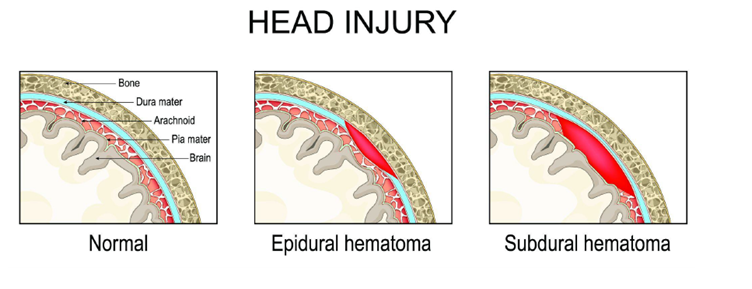
What to expect if a Subdural haematoma scenario is asked;
The NMC OSCE assessment station should be completed within 20 minutes, and you will be provided with a scenario involving a patient with neurological concerns. You may encounter a mannequin or a simulated patient. Your role is to carry out a focused neurological assessment and document the findings.
Step-by-Step Guide to Performing a Neurological Assessment in NMC OSCE
1. Introduction
- Wash your hands by following the 7 steps recommended by WHO
- Introduce yourself.
- Confirm the patient’s identity and allergy status.
- Explain the procedure and gain consent.
- Check pain status.
2. Assess Level of Consciousness
Use the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS):
The GCS stands for Glasgow Coma Scale. It is a tool for the assessment of impairment of the conscious level in response to defined stimuli. It is usually used when a patient is having any neurological illness. The GCS assesses a patient based on their ability to perform eye movement, verbal response, and movement of their body.
- Eye Opening (E) – scored from 1 to 4
- Verbal Response (V) – scored from 1 to 5
- Motor Response (M) – scored from 1 to 6
| Category | Score | Description |
| Eye Opening (E) | 4 | Spontaneous (eyes open without any stimulus) |
| 3 | To Sound (eyes open to verbal command) | |
| 2 | To Pressure (eyes open to painful stimulus) | |
| 1 | None (no eye-opening) | |
| Verbal Response (V) | 5 | Oriented (answers questions correctly) |
| 4 | Confused (converses but is disoriented, answers not entirely correct) | |
| 3 | Inappropriate Words (speak words, but they are not clear) | |
| 2 | Sounds (moans or makes sounds without clear words) | |
| 1 | None (no verbal response) | |
| Motor Response (M) | 6 | Obeys Commands (follows instructions) |
| 5 | Localizes to Pain (Response to painful stimuli) | |
| 4 | Normal Flexion (pulls limb away from painful stimulus) | |
| 3 | Abnormal Flexion (Flexed Posturing) | |
| 2 | Extension to Pain | |
| 1 | None (no motor response) |
A total score out of 15 is given for neurological status.
3. Pupil Assessment
Use a pen torch to assess:
- Size, shape, equality
- Reaction to light
- Describe findings (e.g., “Pupils equal and reactive to light – PEARL”)
Compare pupil size with the given reference size of pupil on the chart.

Download Marking Criteria
Enter the status of your OSCE preparation to get customized OSCE Updates and Tips
4. Motor Function and Limb Strength
Ask the patient to:
- Raise each arm and leg against gravity
- Push and pull against your resistance
Muscle power check for both legs and both arms;
- Normal power
- Mild weakness
- Severe weakness
- Spastic flexion
- Extension
- No movement
5. Vital Signs
Check the vital signs of the patient:
- Blood pressure
- Pulse rate
- Respiratory rate
- Oxygen saturation
- Temperature
6. Documentation
- Record all findings clearly and accurately on the provided GCS chart.
- Document Date and time on the chart
- Document total score and initial.
Tips to follow;
- Practice regularly using NMC OSCE scenarios.
- Verbalize your action or findings clearly during the station.
- Maintain professional communication with the patient.
The Neurological Assessment station in the NMC OSCE is a test not only of your skills but also of your ability to think critically and communicate effectively. By following a structured approach and staying calm under pressure, you can approach this station with confidence.
Remember, the goal is to ensure patient safety, identify neurological deterioration early, and identify the need for the appropriate action.
NMC OSCE For nurses Everything You Need to Know in 2025 Click Here
For Any NMC OSCE Related Queries and Training Chat with Us!