The Nursing and Midwifery Council (NMC) Objective Structured Clinical Examination (OSCE) is a critical step for internationally educated nurses seeking registration in the UK. Among the various clinical skills tested, the Intravenous (IV) flush and Visual Infusion Phlebitis (VIP) score station is an essential component, ensuring that candidates demonstrate safe and effective management of IV therapy.
Administering an IV flush is a routine but crucial nursing procedure that prevents catheter blockage and maintains the patency of the IV line. The VIP scoring system, on the other hand, helps assess the health of the patient’s vein and detect early signs of phlebitis, ensuring timely intervention and prevention of complications.
In the OSCE exam, candidates are expected to demonstrate competence in both these areas by following the appropriate guidelines, ensuring patient safety, and adhering to infection control protocols.

Key Steps in NMC OSCE Intravenous (IV) flush Administration
The IV flush procedure must be performed safely to prevent complications. Here are the key steps:
- Confirm the Prescription and Patient Identity:
- Verify the prescription for the IV flush (type, volume, and frequency) against the patient’s medical chart.
- Confirm the patient’s identity using the three-point check (name, date of birth, hospital/NHS number).
- Gather the Required Equipment:
- 10 mL Pre-filled syringe with 0.9% normal saline
- Alcohol swab
- Gloves and apron
- Hand Hygiene and Infection Control:
- Perform hand hygiene using the WHO’s seven moments of hand hygiene
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) (gloves and apron)
- Check IV Site and Assess for Phlebitis (VIP Score):
- Inspect the IV site for signs of Phlebitis
o Erythema: Redness around the insertion site.
o Oedema: Swelling around the insertion site.
o Pain: Discomfort or pain reported by the patient.
o Pyrexia: Increased warmth or Temperature.
o Palpable Cord: A hard, vein-like structure palpable under the skin.
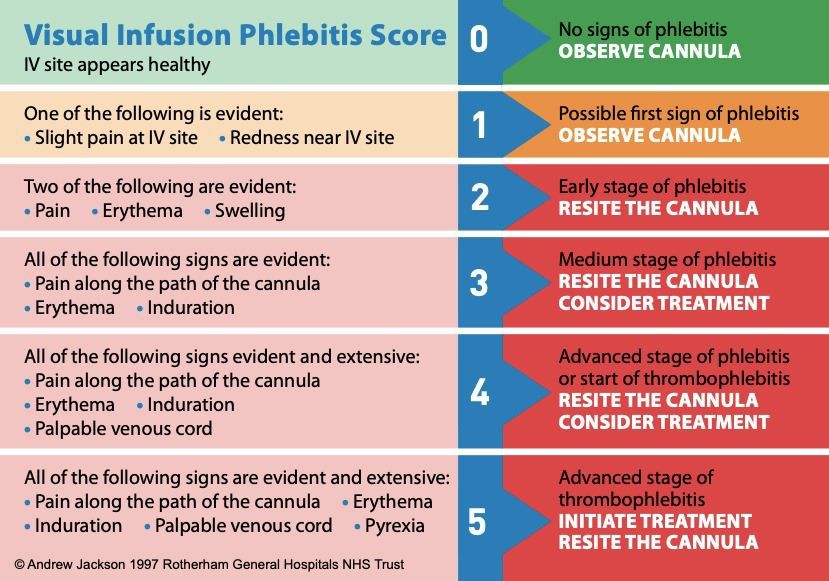
- If phlebitis is Grade 2 or higher, the IV site must be Resite, and medical advice needed.
- Prepare the Syringe and Flush the IV Line:
- Remove air bubbles from the syringe to prevent air embolism
- Clean the IV access port using an alcohol swab for 30 seconds and let it dry
- Connect the syringe and flush using a pulsatile technique (push-pause method) to prevent catheter occlusion
- Dispose of Equipment and Document the Procedure:
- Dispose of the syringe and gloves appropriately
- Document the procedure in the patient’s chart accurately
Common Mistakes to Avoid in NMC OSCE Intravenous (IV) flush Administration
Candidates often make the following mistakes during the IV flush and VIP score station in the NMC OSCE:
- Failing to perform hand hygiene properly before and after the procedure
- Not assessing the IV site before flushing, which could lead to worsening complications
- Not removing air bubbles from the syringe, increasing the risk of air embolism
- Flushing too forcefully, which can cause vein damage or dislodge the catheter
Tips for Success in the Intravenous (IV) flush and Visual Infusion Phlebitis (VIP)
- Practice regularly using a simulated IV line to get comfortable with the technique.
- Memorize the VIP scoring system and use it consistently for all IV site assessments.
- Follow a systematic approach – assessment, preparation, flushing, and documentation.
- Speak out loud during the exam, explaining what you are doing to demonstrate knowledge and confidence.
- Ensure effective communication with the patient, explaining the procedure and gaining consent before proceeding.
- Stay calm and focused, ensuring that you adhere to infection control measures at all times.

The NMC OSCE Intravenous (IV) flush and Visual Infusion Phlebitis (VIP) is a crucial part of the NMC OSCE exam, testing a nurse’s ability to manage IV therapy safely. By following the correct technique, avoiding common mistakes, and demonstrating confidence, candidates can successfully clear this station. Regular practice and thorough understanding of the procedure will significantly improve performance and patient safety outcomes.
By mastering these key steps, internationally trained nurses can enhance their skills and increase their chances of passing the NMC OSCE exam successfully.
NMC OSCE For nurses Everything You Need to Know in 2025👉 Click Here
For Any NMC OSCE Related Queries and Training Chat with Us!









